深入Istio系列-Sidecar自动注入
Sidecar 自动注入机制是将 sidecar 代理自动添加到用户创建的 pod。
它使用 MutatingWebhook 机制在 pod 创建的时候将 sidecar 的容器和卷添加到每个 pod 的模版里。
用户可以通过 webhooks namespaceSelector 机制来限定需要启动自动注入的范围,也可以通过注解的方式针对每个 pod 来单独启用和禁用自动注入功能。
Sidecar 是否会被自动注入取决于下面 3 条配置和 2 条安全规则:
配置:
- webhooks namespaceSelector
- 默认策略 policy
- pod 级别的覆盖注解
安全规则:
- sidecar 默认不能被注入到 kube-system 和 kube-public 这两个 namespace
- sidecar 不能被注入到使用 host network 网络的 pod 里
下面的表格展示了基于上述三个配置条件的最终注入状态。上述的安全规则不会被覆盖。
| namespaceSelector 匹配 | 默认策略 | sidecar.istio.io/inject 注解 | Sidecar 是否注入 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 是 | enabled | true (default) | 是 |
| 是 | enabled | false | 否 |
| 是 | disabled | true | 是 |
| 是 | disabled | false (default) | 否 |
| 否 | enabled | true (default) | 否 |
| 否 | enabled | false | 否 |
| 否 | disabled | true | 否 |
| 否 | disabled | false (default) | 否 |
以下内容基于Istio 1.13.2版本
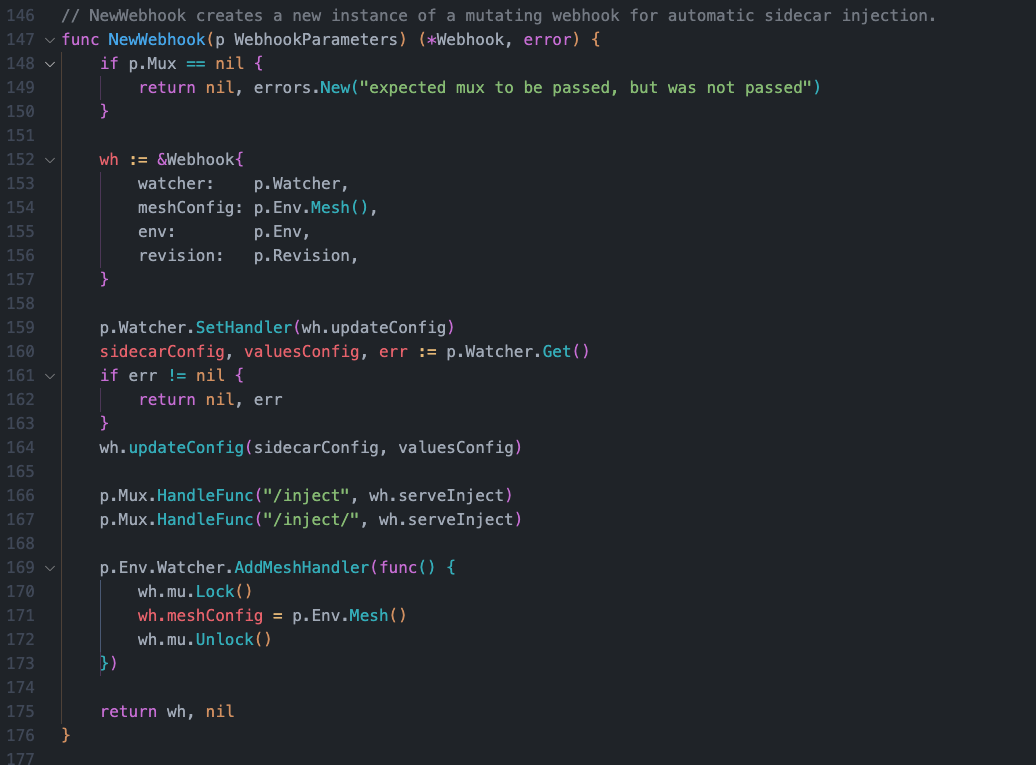
NewWehook方法
pkg/kube/inject/webhook.go
func NewWebhook(p WebhookParameters) (*Webhook, error) {
if p.Mux == nil {
return nil, errors.New("expected mux to be passed, but was not passed")
}
wh := &Webhook{
watcher: p.Watcher,
meshConfig: p.Env.Mesh(),
env: p.Env,
revision: p.Revision,
}
p.Watcher.SetHandler(wh.updateConfig)
sidecarConfig, valuesConfig, err := p.Watcher.Get()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
wh.updateConfig(sidecarConfig, valuesConfig)
//初始化Webhook实例的时候注册/inject对应的处理器
p.Mux.HandleFunc("/inject", wh.serveInject)
p.Mux.HandleFunc("/inject/", wh.serveInject)
p.Env.Watcher.AddMeshHandler(func() {
wh.mu.Lock()
wh.meshConfig = p.Env.Mesh()
wh.mu.Unlock()
})
return wh, nil
}
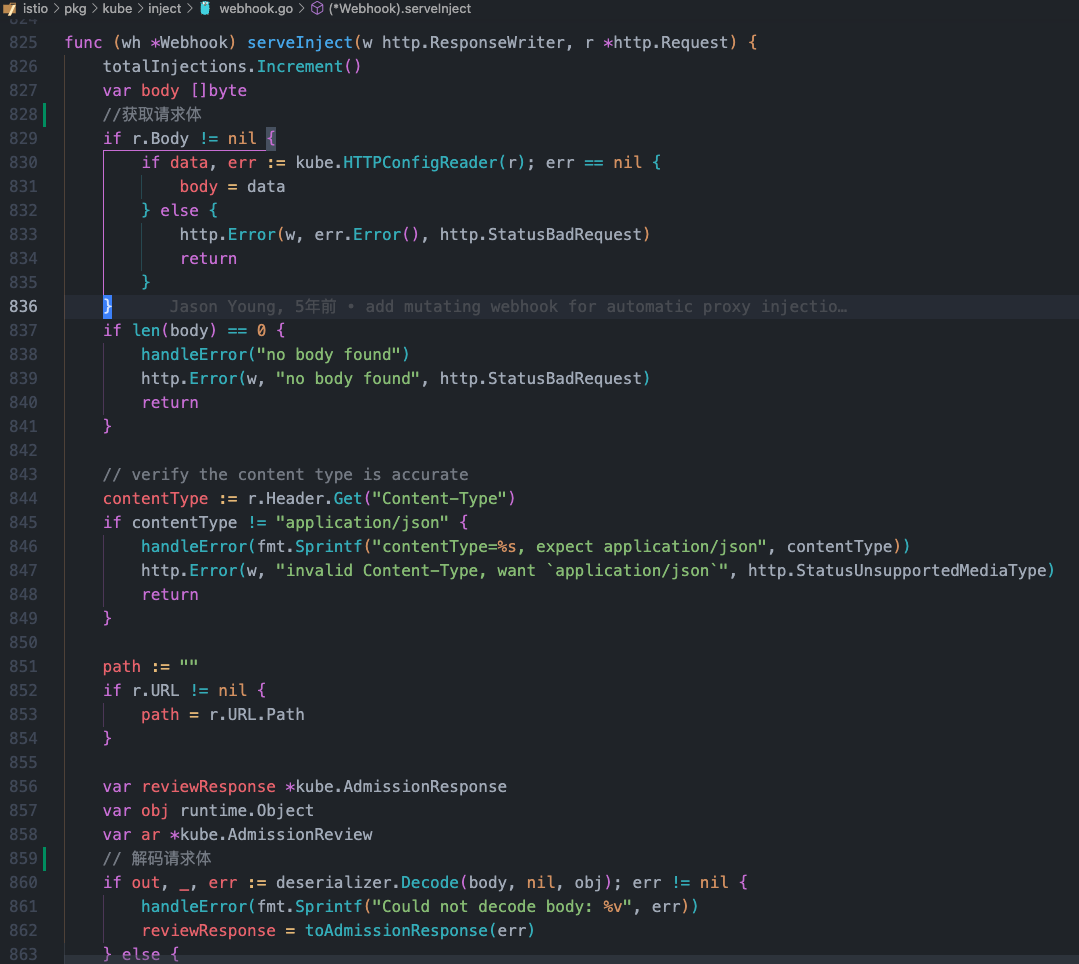
serveInject方法
pkg/kube/inject/webhook.go 大概825-895行
func (wh *Webhook) serveInject(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
totalInjections.Increment()
var body []byte
// 获取请求体
if r.Body != nil {
if data, err := kube.HTTPConfigReader(r); err == nil {
body = data
} else {
http.Error(w, err.Error(), http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
}
if len(body) == 0 {
handleError("no body found")
http.Error(w, "no body found", http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
// verify the content type is accurate
contentType := r.Header.Get("Content-Type")
if contentType != "application/json" {
handleError(fmt.Sprintf("contentType=%s, expect application/json", contentType))
http.Error(w, "invalid Content-Type, want `application/json`", http.StatusUnsupportedMediaType)
return
}
path := ""
if r.URL != nil {
path = r.URL.Path
}
var reviewResponse *kube.AdmissionResponse
var obj runtime.Object
var ar *kube.AdmissionReview
// 解码请求体
if out, _, err := deserializer.Decode(body, nil, obj); err != nil {
handleError(fmt.Sprintf("Could not decode body: %v", err))
reviewResponse = toAdmissionResponse(err)
} else {
log.Debugf("AdmissionRequest for path=%s\n", path)
ar, err = kube.AdmissionReviewKubeToAdapter(out)
if err != nil {
handleError(fmt.Sprintf("Could not decode object: %v", err))
}
// 进入inject方法逻辑判断
reviewResponse = wh.inject(ar, path)
}
response := kube.AdmissionReview{}
response.Response = reviewResponse
var responseKube runtime.Object
var apiVersion string
if ar != nil {
apiVersion = ar.APIVersion
response.TypeMeta = ar.TypeMeta
if response.Response != nil {
if ar.Request != nil {
response.Response.UID = ar.Request.UID
}
}
}
responseKube = kube.AdmissionReviewAdapterToKube(&response, apiVersion)
resp, err := json.Marshal(responseKube)
if err != nil {
log.Errorf("Could not encode response: %v", err)
http.Error(w, fmt.Sprintf("could not encode response: %v", err), http.StatusInternalServerError)
}
if _, err := w.Write(resp); err != nil {
log.Errorf("Could not write response: %v", err)
http.Error(w, fmt.Sprintf("could not write response: %v", err), http.StatusInternalServerError)
}
}
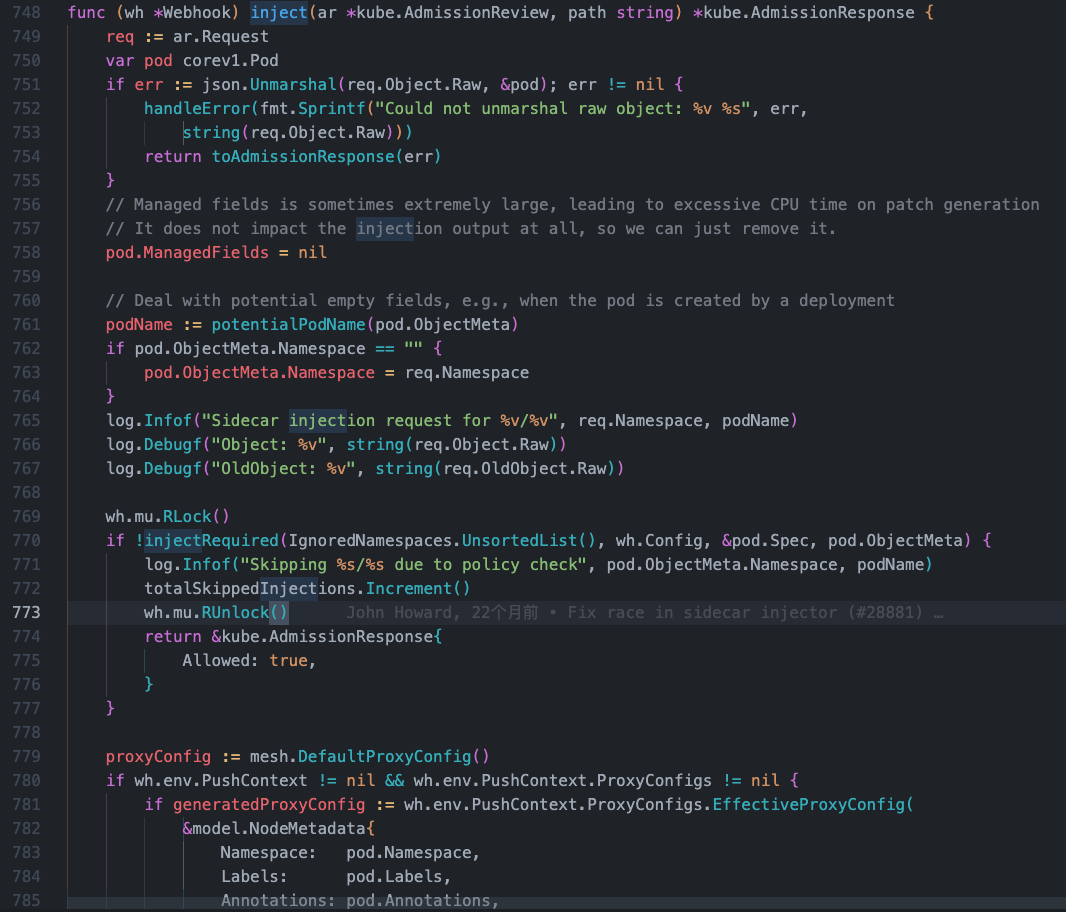
inject方法
pkg/kube/inject/webhook.go 大概在748-823行
func (wh *Webhook) inject(ar *kube.AdmissionReview, path string) *kube.AdmissionResponse {
req := ar.Request
var pod corev1.Pod
if err := json.Unmarshal(req.Object.Raw, &pod); err != nil {
handleError(fmt.Sprintf("Could not unmarshal raw object: %v %s", err,
string(req.Object.Raw)))
return toAdmissionResponse(err)
}
// Managed fields is sometimes extremely large, leading to excessive CPU time on patch generation
// It does not impact the injection output at all, so we can just remove it.
pod.ManagedFields = nil
// Deal with potential empty fields, e.g., when the pod is created by a deployment
podName := potentialPodName(pod.ObjectMeta)
if pod.ObjectMeta.Namespace == "" {
pod.ObjectMeta.Namespace = req.Namespace
}
log.Infof("Sidecar injection request for %v/%v", req.Namespace, podName)
log.Debugf("Object: %v", string(req.Object.Raw))
log.Debugf("OldObject: %v", string(req.OldObject.Raw))
wh.mu.RLock()
// Sicader注入判断逻辑
if !injectRequired(IgnoredNamespaces.UnsortedList(), wh.Config, &pod.Spec, pod.ObjectMeta) {
log.Infof("Skipping %s/%s due to policy check", pod.ObjectMeta.Namespace, podName)
totalSkippedInjections.Increment()
wh.mu.RUnlock()
return &kube.AdmissionResponse{
Allowed: true,
}
}
proxyConfig := mesh.DefaultProxyConfig()
if wh.env.PushContext != nil && wh.env.PushContext.ProxyConfigs != nil {
if generatedProxyConfig := wh.env.PushContext.ProxyConfigs.EffectiveProxyConfig(
&model.NodeMetadata{
Namespace: pod.Namespace,
Labels: pod.Labels,
Annotations: pod.Annotations,
}, wh.meshConfig); generatedProxyConfig != nil {
proxyConfig = *generatedProxyConfig
}
}
deploy, typeMeta := kube.GetDeployMetaFromPod(&pod)
params := InjectionParameters{
pod: &pod,
deployMeta: deploy,
typeMeta: typeMeta,
templates: wh.Config.Templates,
defaultTemplate: wh.Config.DefaultTemplates,
aliases: wh.Config.Aliases,
meshConfig: wh.meshConfig,
proxyConfig: &proxyConfig,
valuesConfig: wh.valuesConfig,
revision: wh.revision,
injectedAnnotations: wh.Config.InjectedAnnotations,
proxyEnvs: parseInjectEnvs(path),
}
wh.mu.RUnlock()
patchBytes, err := injectPod(params)
if err != nil {
handleError(fmt.Sprintf("Pod injection failed: %v", err))
return toAdmissionResponse(err)
}
reviewResponse := kube.AdmissionResponse{
Allowed: true,
Patch: patchBytes,
PatchType: func() *string {
pt := "JSONPatch"
return &pt
}(),
}
totalSuccessfulInjections.Increment()
return &reviewResponse
}
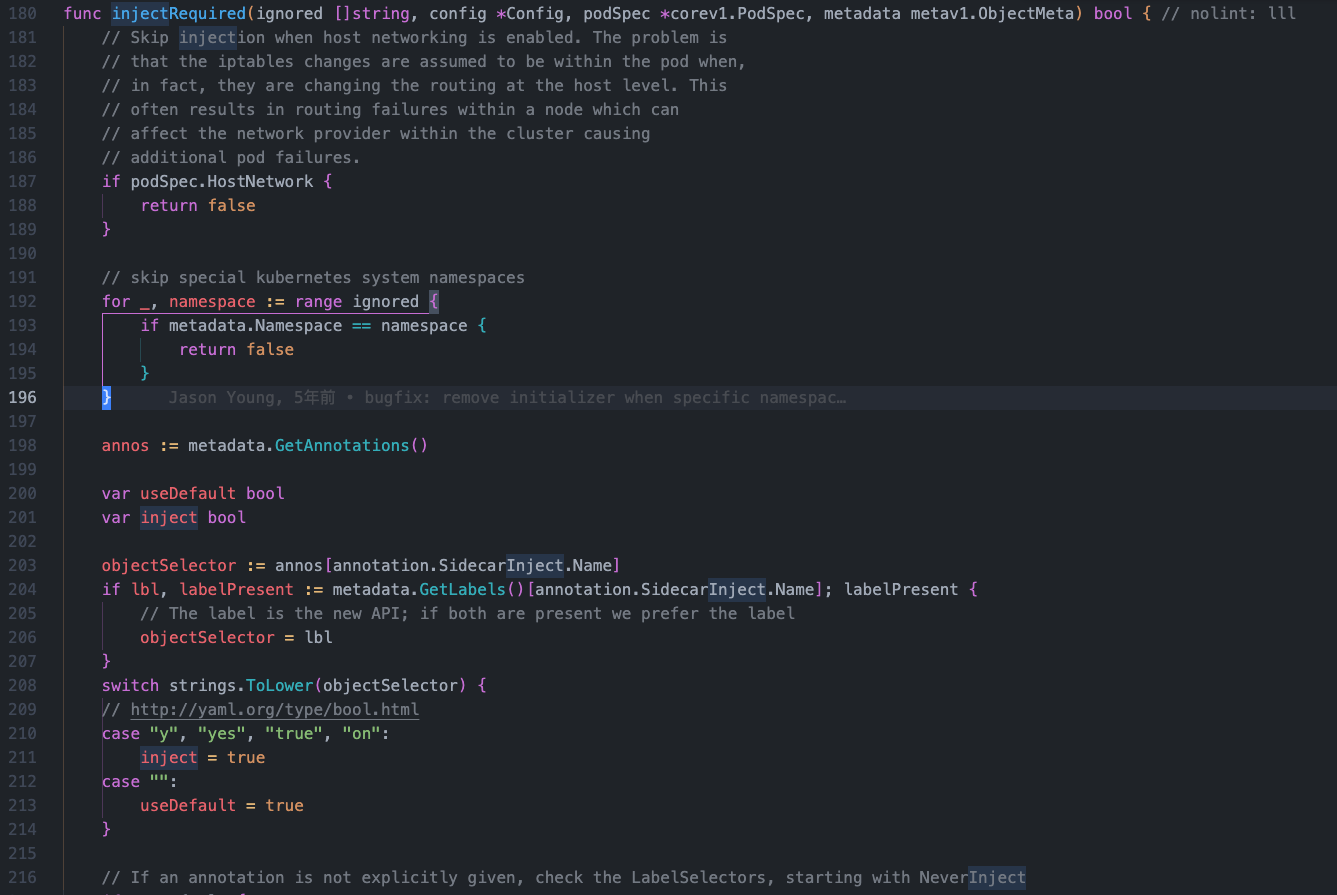
injectRequired方法
pkg/kube/inject/inject.go 大概在180-290行
func injectRequired(ignored []string, config *Config, podSpec *corev1.PodSpec, metadata metav1.ObjectMeta) bool { // nolint: lll
// Skip injection when host networking is enabled. The problem is
// that the iptables changes are assumed to be within the pod when,
// in fact, they are changing the routing at the host level. This
// often results in routing failures within a node which can
// affect the network provider within the cluster causing
// additional pod failures.
// 主机网络模式不注入sicader
if podSpec.HostNetwork {
return false
}
// skip special kubernetes system namespaces
// kube-system、kube-public、kube-node-lease、local-path-storage四个名称空间不被注入sicader
for _, namespace := range ignored {
if metadata.Namespace == namespace {
return false
}
}
annos := metadata.GetAnnotations()
var useDefault bool
var inject bool
// annotation 是否开启注入 `sidecar.istio.io/inject: "true"`
objectSelector := annos[annotation.SidecarInject.Name]
if lbl, labelPresent := metadata.GetLabels()[annotation.SidecarInject.Name]; labelPresent {
// The label is the new API; if both are present we prefer the label
objectSelector = lbl
}
switch strings.ToLower(objectSelector) {
// http://yaml.org/type/bool.html
case "y", "yes", "true", "on":
inject = true
case "":
useDefault = true
}
// If an annotation is not explicitly given, check the LabelSelectors, starting with NeverInject
// 判断 configmap `istio-sidecar-injector` NeverInject 匹配标签选择器
if useDefault {
for _, neverSelector := range config.NeverInjectSelector {
selector, err := metav1.LabelSelectorAsSelector(&neverSelector)
if err != nil {
log.Warnf("Invalid selector for NeverInjectSelector: %v (%v)", neverSelector, err)
} else if !selector.Empty() && selector.Matches(labels.Set(metadata.Labels)) {
log.Debugf("Explicitly disabling injection for pod %s/%s due to pod labels matching NeverInjectSelector config map entry.",
metadata.Namespace, potentialPodName(metadata))
inject = false
useDefault = false
break
}
}
}
// If there's no annotation nor a NeverInjectSelector, check the AlwaysInject one
// 判断 configmap `istio-sidecar-injector` AlwaysInject 匹配标签选择器
if useDefault {
for _, alwaysSelector := range config.AlwaysInjectSelector {
selector, err := metav1.LabelSelectorAsSelector(&alwaysSelector)
if err != nil {
log.Warnf("Invalid selector for AlwaysInjectSelector: %v (%v)", alwaysSelector, err)
} else if !selector.Empty() && selector.Matches(labels.Set(metadata.Labels)) {
log.Debugf("Explicitly enabling injection for pod %s/%s due to pod labels matching AlwaysInjectSelector config map entry.",
metadata.Namespace, potentialPodName(metadata))
inject = true
useDefault = false
break
}
}
}
var required bool
// 判断 configmap `istio-sidecar-injector` 默认策略policy
switch config.Policy {
default: // InjectionPolicyOff
log.Errorf("Illegal value for autoInject:%s, must be one of [%s,%s]. Auto injection disabled!",
config.Policy, InjectionPolicyDisabled, InjectionPolicyEnabled)
required = false
case InjectionPolicyDisabled:
if useDefault {
required = false
} else {
required = inject
}
case InjectionPolicyEnabled:
if useDefault {
required = true
} else {
required = inject
}
}
if log.DebugEnabled() {
// Build a log message for the annotations.
annotationStr := ""
for name := range AnnotationValidation {
value, ok := annos[name]
if !ok {
value = "(unset)"
}
annotationStr += fmt.Sprintf("%s:%s ", name, value)
}
log.Debugf("Sidecar injection policy for %v/%v: namespacePolicy:%v useDefault:%v inject:%v required:%v %s",
metadata.Namespace,
potentialPodName(metadata),
config.Policy,
useDefault,
inject,
required,
annotationStr)
}
return required
}